Do Hot Air Balloons Run With Convection Heat Transfer?

If you’re curious about hot air balloons and how they manage to rise, you might be wondering whether they rise through a conduction, convection or radiation process?
Well, hot air balloons do indeed rise through a form of convection, not conduction or radiation, this is a form of buoyancy convection since the hot air inside of the balloon becomes less dense than the air around it, causing it to rise.
In our guide below, we will explain in more detail exactly how hot air balloons work through convection, as well as a few other examples of how convection works in everyday items, we will also discuss why conduction and radiation are different and how to make your own convection hot air balloon.
How Do Hot Air Balloons Work Through Convection?
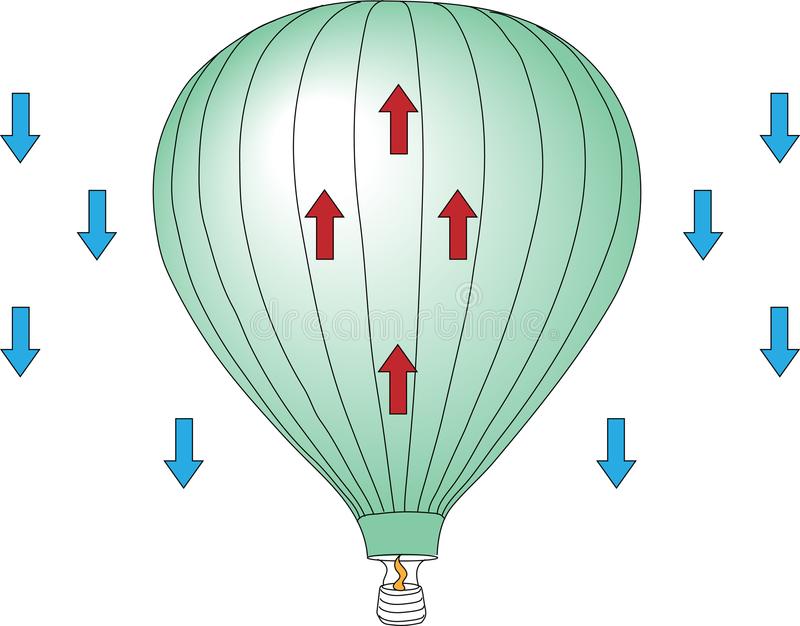
As we mentioned above, hot air balloons work through a moving convection process rather than radiation and conduction.
Convection in its simplest form is the transfer of heat through circulating air and liquids, this works inside of a hot air balloon by heating the inside of the air with a burner located at the bottom of the balloon, this then makes the air inside of the balloon less dense or lighter than the cooler air on the outside, causing the balloon to float upwards.
Examples Of Convection
- Boiling water – Heat circulates at the bottom of the pot you are heating, the hot water rises while the colder water in the pan moves to the bottom in a circular motion.
- Thawing frozen food – When frozen food is placed under running water it cools quicker than when placed still in cold water.
- Forced convection – Anything forced with a pump or fan is a form of convection, this can be seen in air conditioning or a convection oven for example.
What Are Radiation And Conduction?
Now we know about how convection and hot air balloons work, let’s explore the difference between this heat transfer with radiation and conduction.
- Radiation – This is where energy comes in the forms of waves and rays, it is either reflected or absorbed and can increase the heat of an object when absorbed. For example, the sun emits radiation which is then absorbed by the heat of the earth.
- Conduction – A form of thermal energy heat transfer which happens when two particles directly touch each other, most of the time this happens in solid particles, heat transfer happens at one end and bumps the next particles causing kinetic energy transfer.
How To Make Your Own Convection Hot Air Balloon
To understand more about how convection works in hot air balloons we’ve put together a small science experiment to try out at home below with your hot air balloon, this will show how the convection current causes the balloon to rise.
Equipment
- 10 sheets of tissue paper which measure 20-inches x 30-inches.
- A glue stick.
- Scissors.
- Hair dryers.
- Marker.
- 20-inch x 30-inch tag board.
- Heavy paper strip.
Method
- First start to create your hot air balloon template with the tagboard material, keep in mind a teardrop shape, it should be around 25-inches tall and have a 3.5-inch base.
- Now take five sheets of tissue paper and layer them over one another, take the long side then fold in half, take your marker and template to make the teardrop shape, cut it out then repeat with the other 5 sheets that you have, decorate if desired.
- Pick two layers of your paper then glue them together with your stick and repeat with other panels until you make a balloon shape. Make sure there are no holes in your seal.
- Take the heavy paper strip and glue it to the inside of the balloon at the opening in a looped shape.
- Now, with your hair dryer on the low setting, fill the made balloon with hot air, holding it over the hair dryer, not too tightly.
- The balloon will now rise through convection, and as the air cools will drift back down.
Frequently Asked Questions About Hot Air Balloons & Convection
What’s the difference between gas hot air balloons and burners?
Hot air balloons work in two ways, either through a gas such as helium or hydrogen operating closed or through hot air convection from a burner at the base which we discussed above.
What are the parts of a hot air balloon?
The main parts of a hot air balloon are its envelope or balloon as it’s called, the balloon basket and the balloon burner which is essentially the engine of the hot air balloon, causing it to rise through convection.
Can you steer a hot air balloon?
Hot air balloons cannot be steered by a plane but can be moved by the wind instead, pilots use this to manoeuvre the balloon left or right.
How do hot air balloons land with heat transfer?
For the landing, hot air balloons have a vent at the top of the balloon which is released to allow the hot air to escape, making the air heavier inside, causing it to land.
What type of convection does a hot air balloon have?
Hot air balloons use a convection current for heat transfer, this makes the air inside lighter and warmer as it floats upwards through a term called buoyancy.
Do hot air balloons emit radiation?
Hot air balloons do have some radiation loss when they are heated but do not emit radiation through their heat transfer, most heat is lost through the convection process.
Final Words
To conclude, hot air balloons rise through the process of hot air convection, not through radiation or conduction. This happens as the burner heats the air inside of the balloon or ‘envelope’, making the air less dense inside than the cooler air on the outside.
Releasing or containing the hot air inside of the balloon allows the equipment to move up or down according to the vents on the balloon, for landing, the hot air would be released to make the balloon heavier.
I’m Annie, a twenty-something year old girl who loves hot air balloons. So much so, that I have a full time job as a Flight Instructor and it is all I love talking about. Something about being up there in the elevated altitudes helps all my stresses float away!